John MacGillivray was a Scottish naturalist who lived
from 1822 to 1867. He was a prolific collector and explorer, and is best known
for his travels to Australia and the Pacific, where he collected and documented
a vast array of plant and animal species.
 |
| John MacGillivray |
In 1848, MacGillivray was invited by the British government to join the HMS Rattlesnake as the naturalist on an expedition to the Australian coast. The Rattlesnake spent three years mapping the coast of Australia and the Pacific, and during this time, MacGillivray collected and documented an enormous number of specimens, including birds, insects, plants, and marine life.
 |
| HMS Rattlesnake |
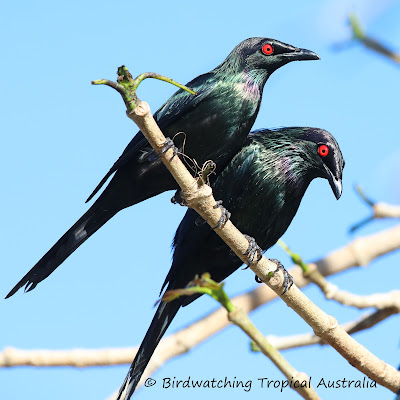
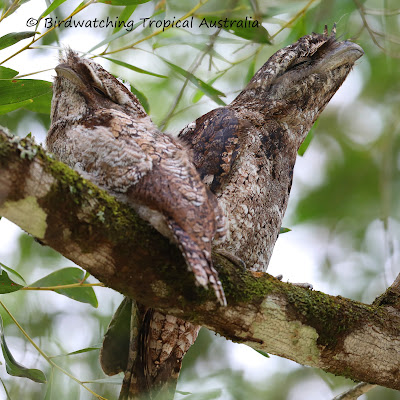
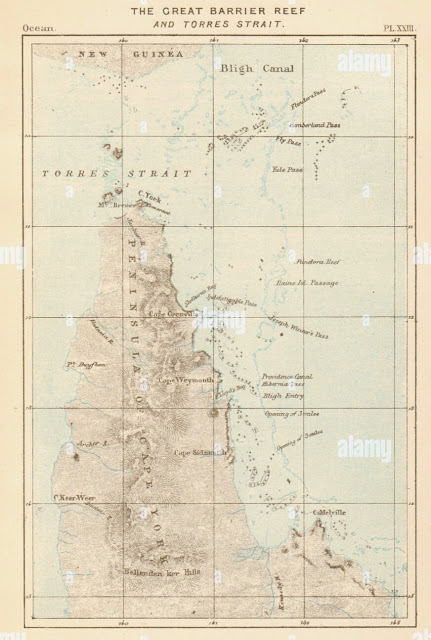
One of the most significant areas of MacGillivray's collecting work was the Cape York Peninsula, located in the far north of Queensland, Australia. This remote and rugged region was largely unexplored at the time, and MacGillivray's work there was critical in helping to build our understanding of the natural history of the area.
MacGillivray's bird collecting work on the Cape York Peninsula
was particularly noteworthy. During his time there, he collected over 500 bird
specimens, representing around 90 species. Many of these were new to science,
and MacGillivray's work helped to establish the region as a critical area for
bird diversity and conservation.
MacGillivray was an incredibly meticulous and dedicated collector, and his notes and observations from his time on the Cape York Peninsula provide a fascinating window into the world of 19th-century naturalism. For example, he recorded detailed notes on the diet and habitat preferences of different bird species, as well as their behaviours and vocalizations. He also realised that the development of relationships with local Indigenous peoples were critical to the success of his work. Not simply guides, they had an enormous collective experience of their own natural world. MacGillivray was always at great pains to ensure, where possible, the local dialectal name was recorded for any specimen he collected.
One of the most significant bird species that
MacGillivray collected on the Cape York Peninsula was the Golden-shouldered Parrot
(Psephotus chrysopterygius). This colourful bird is endemic to the Cape York
Peninsula and is listed as endangered due to habitat loss and fragmentation.
MacGillivray's early collections of this species provided important information
about its distribution, ecology, and behaviour, and continue to inform
conservation efforts today.
 |
| Golden-shouldered Parrot |
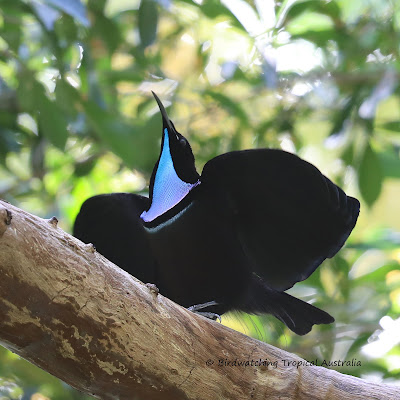
The following is an account by expedition naturalist John MacGillivray from the Narrative of the Voyage of HMS Rattlesnake 1846-1850 Vol I. pp. 323–325. It describes the first recorded observation and specimen collection of the Fawn-breasted Bowerbird Chlamydera cerviniventris:-
″Two days before we left Cape York I was told that some bower-birds had been seen in a thicket, or patch of low scrub, half a mile from the beach, and after a long search I found a recently constructed bower, four feet long and eighteen inches high, with some fresh berries lying upon it. The bower was situated near the border of the thicket, the bushes composing which were seldom more than ten feet high, growing in smooth sandy soil without grass.Next morning I was landed before daylight, and proceeded to the place in company with Paida, taking with us a large board on which to carry off the bower specimen. I never before met with a more wary bird, and for a long time it enticed me to follow it to a short distance, then flying off and alighting on the bower, it would deposit a berry or two, run through, and be off again (as the black told me) before I could reach the spot. At length, just as my patience was being exhausted, I saw the bird enter the bower and disappear, when I fired at random through the twigs, fortunately with effect. So closely had we concealed ourselves latterly, and so silent had we been, that a kangaroo while feeding actually hopped up within fifteen yards, unconscious of our presence until fired at. My bower-bird proved to be a new species, since described by Mr Gould as Chlamydera cerviniventris, and the bower is exhibited in the British Museum."
Despite these challenges, MacGillivray's work on the Cape York Peninsula remains a remarkable achievement. His collections and observations provide a critical foundation for our understanding of the natural history of the region, and his legacy continues to inspire and inform scientists and conservationists today.
In conclusion, John MacGillivray's collecting work on the
Cape York Peninsula in Australia was a significant contribution to the field of
natural history. His meticulous observations and collections of bird species
provided important insights into the ecology and behaviour of these animals,
and helped to establish the region as a critical area for conservation. Today,
his legacy continues to inspire and inform scientists and conservationists as
we work to better understand and protect the natural world.